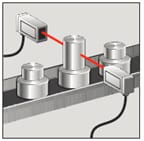
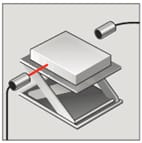
Through-beam sensing, also known as transmitted beam, opposed mode, direct-scanning, or break-beam is usually the first choice in solving photoelectric applications. These sensors can detect objects independent of color, reflectivity and are not affected by second surface reflections. The high gain of these sensors will burn through smoke, fog, haze, dust, mist, coolant, and dirt allowing them to be used in harsh or contaminated environments.
The emitter and receiver are in separate housings and are aimed directly opposite each other or in direct line of sight. When the target breaks the light beam, which can be infrared, visible red or laser, the output is activated. Through-beam sensors offer the longest sensing range of up to 100 meters. The target should be larger than the effective beam or if the application requires detecting smaller parts, apertures can be added.
Applications
- Stack height
- Conveyors, package detection
- Skewed lid detection
- Parts counting
- Tool verification
- Part presence
- Error proofing